WGS/WES
We provide complete whole genome and exome sequencing (WGS/WES) analysis pipelines based on GATK Best Practices. Our pipeline supports both germline and somatic variant discovery, including quality control, alignment, variant calling, annotation, and interpretation of clinically or biologically relevant variants.
Workflow Summary
---
config:
theme: 'base'
themeVariables:
fontFamily: 'verdana'
fontSize: '25px'
---
flowchart LR
subgraph Preprocessing["`**Preprocessing**`"]
direction TB
Raw[Raw Reads]
QC[Quality Control]
Align[Alignment]
Sort[Sorting]
RG[Read Group Fixing]
Dedup[Mark Duplicates]
BQSR[Base Quality Recalibration]
Raw --> QC --> Align --> Sort --> RG --> Dedup --> BQSR
end
subgraph VariantCalling["`**Variant Calling**`"]
direction TB
Haplotype["Germline Calling (HaplotypeCaller)"]
Mutect["Somatic Calling (Mutect2)"]
JointGenotyping[Joint Genotyping]
Filter[Filtering]
Haplotype --> JointGenotyping --> Filter
Mutect --> Filter
end
subgraph Annotation["`**Annotation**`"]
direction TB
VEP[VEP Annotation]
Func["Functional Annotation (Funcotator)"]
Prioritize[Variant Prioritization]
Report[Summary & Reporting]
VEP --> Func --> Prioritize --> Report
end
Preprocessing --> VariantCalling --> Annotation
Preprocessing
- Raw Reads: Input raw sequencing data (FASTQ).
- Quality Control: Assess read quality and remove low-quality bases or reads.
- Alignment: Map reads to the reference genome using BWA-MEM.
- Sorting: Sort aligned reads by genomic coordinates.
- Read Group Fixing: Add or correct read group information.
- Mark Duplicates: Identify and mark PCR duplicates.
- Base Quality Recalibration: Adjust base quality scores using known variants.
Variant Calling
- Germline Variant Calling: Use HaplotypeCaller for SNVs and indels in germline samples.
- Somatic Variant Calling: Use Mutect2 for paired tumor-normal analysis.
- Joint Genotyping: Combine gVCF files for cohort-level calling.
- Variant Filtering: Apply quality and artifact filters.
Annotation & Interpretation
- VEP Annotation: Functional consequence prediction using Ensembl VEP.
- Funcotator: Integrate additional clinical and biological annotations.
- Variant Prioritization: Highlight potential pathogenic or relevant variants.
- Summary & Reporting: Provide visual and tabular summaries of findings.
Example
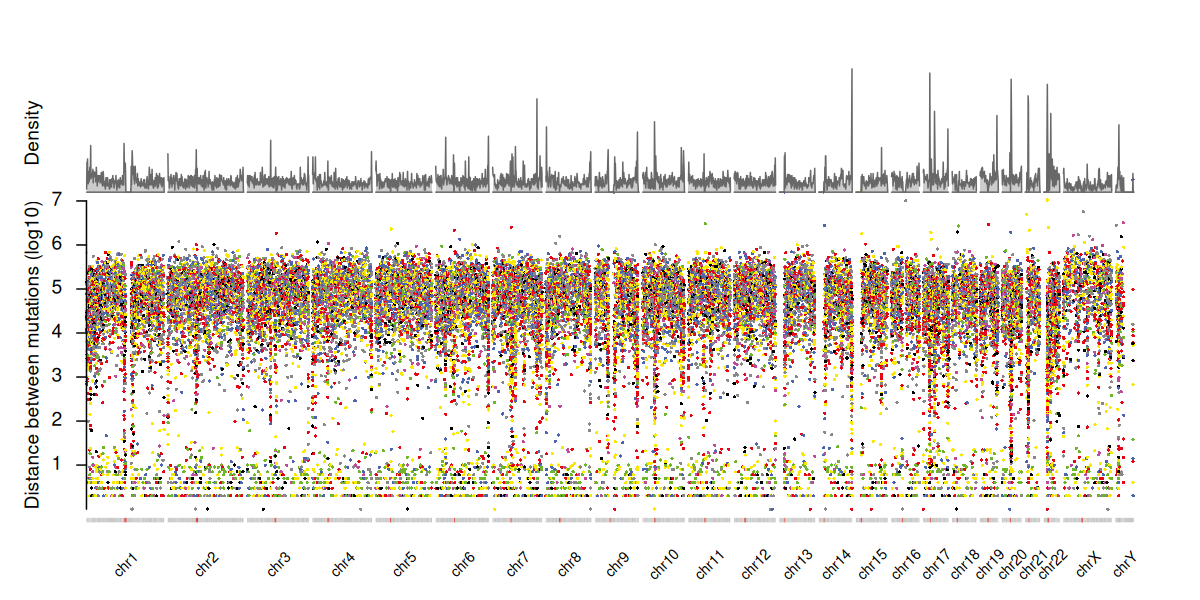
Principal component analysis (PCA) can be used to assess batch effects or sample stratification based on genotypic data.
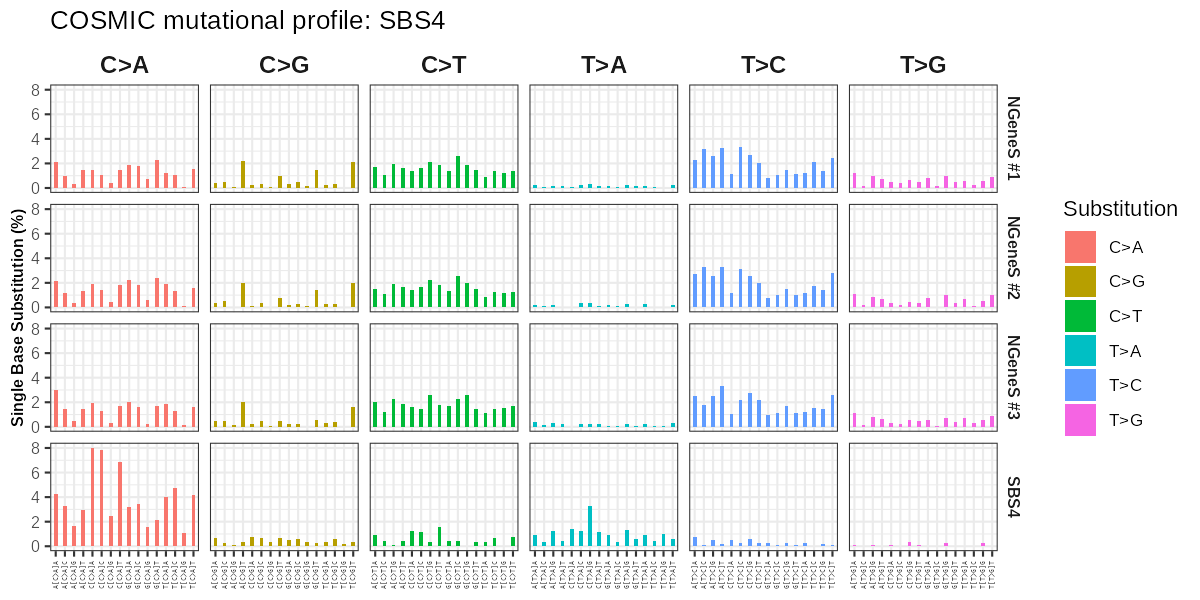
COSMIC mutational signatures are characteristic patterns of somatic mutations observed across cancer genomes. Each signature reflects distinct mutational processes, such as exposure to carcinogens, defective DNA repair mechanisms, or aging-related changes.
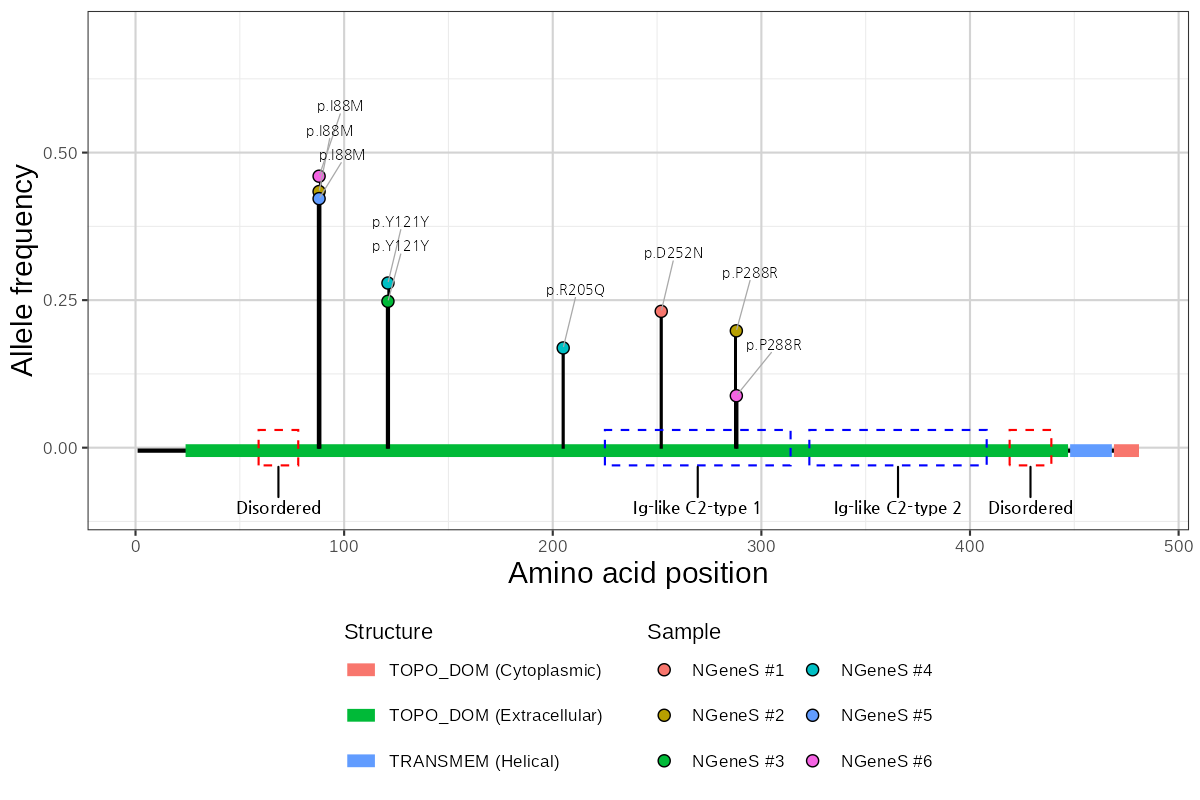
The structural context of a variant within a protein is critical for interpreting its potential functional impact. Our visualization integrates variant position, allele frequency, and protein domain architecture to provide an intuitive and information-rich representation. We deliver publication-ready figures of the highest quality, enabling researchers to readily interpret and present their data with confidence.
For detailed options and customization, contact us.